The Expanding Reality: A Deep Dive into XR technology
Extended Reality (XR) is rapidly evolving, blurring the lines between the physical and digital worlds. It encompasses a spectrum of immersive technologies, including Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR). This convergence is transforming industries, redefining entertainment, and reshaping how we interact with information. Let’s explore the intricacies of XR, its applications, and its potential impact on our future.
XR isn’t a monolithic entity; it’s a collective term representing a continuum of immersive experiences:
Virtual Reality (VR): Immersion into Digital Worlds
VR creates entirely simulated environments, transporting users to virtual realms. Through headsets and controllers, users can interact with these digital spaces, feeling as though they’re physically present. VR’s ability to create a sense of presence is its defining characteristic.
Augmented Reality (AR): Overlaying Digital Information onto the Real World
AR enhances the real world by overlaying digital information onto our perception. Using devices like smartphones or AR glasses, users can see virtual elements integrated into their physical surroundings. AR adds a layer of digital augmentation to our existing reality.

Mixed Reality (MR): Blending the Physical and Digital
MR combines elements of both VR and AR, allowing digital objects to interact with the real world in real time. Unlike AR’s simple overlay, MR anchors virtual elements into the physical environment, creating a more seamless and interactive experience. MR enables digital and physical objects to coexist and interact.
Several core technologies enable the creation of immersive XR experiences:
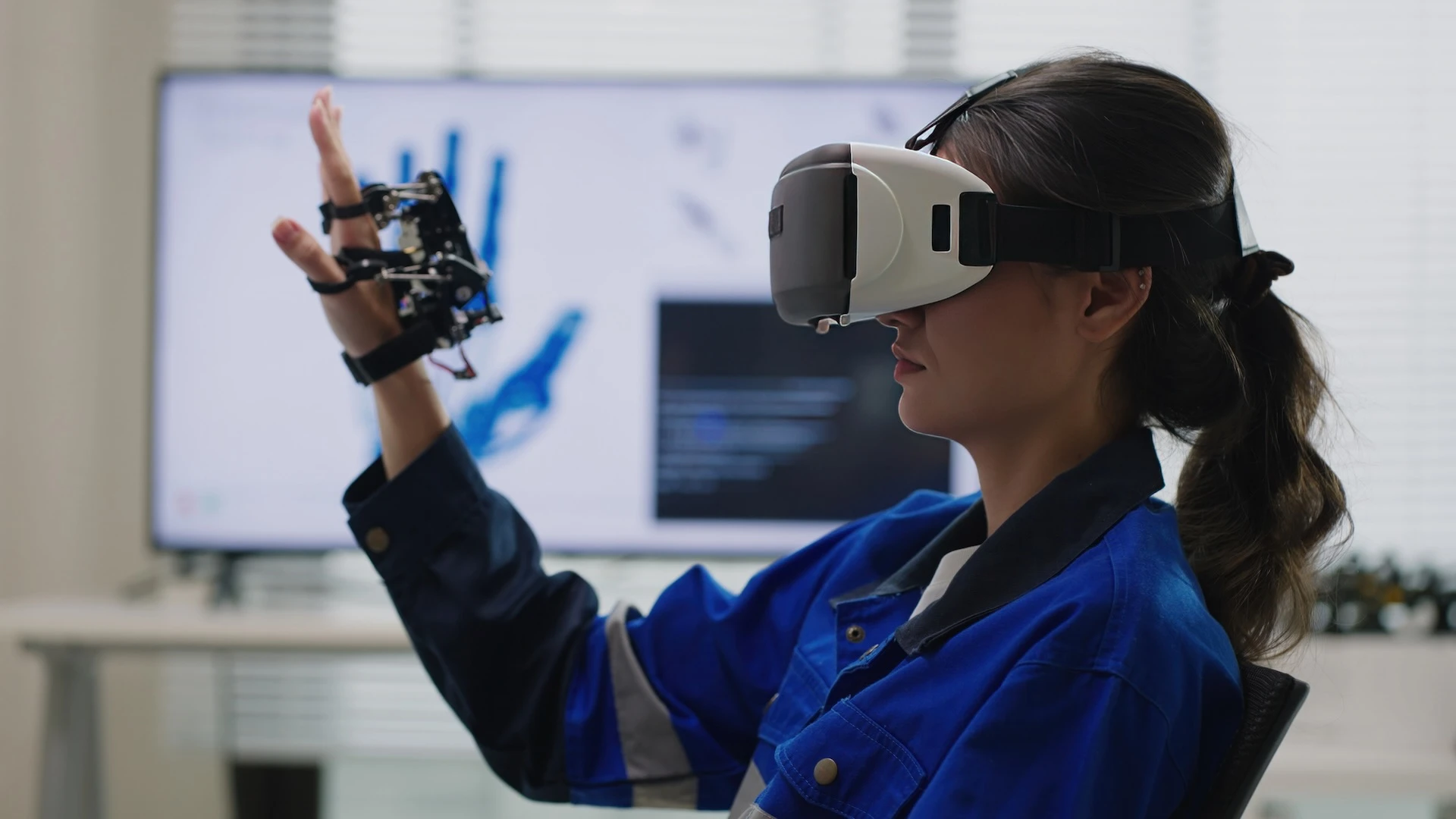
Head-Mounted Displays (HMDs)
HMDs are the primary hardware for VR and some MR experiences, providing visual and auditory immersion. They range from tethered headsets requiring a powerful computer to standalone devices offering wireless freedom.
Spatial Tracking and Mapping
Accurate spatial tracking and mapping are crucial for seamless XR experiences. They allow the system to understand the user’s position and orientation in the physical or virtual environment, ensuring realistic interactions.
Input Devices
Input devices, such as hand controllers, gesture recognition, and voice commands, enable users to interact with XR environments. These devices facilitate navigation, manipulation of virtual objects, and communication within immersive spaces.
Rendering and Graphics Processing
Powerful rendering and graphics processing capabilities are essential for creating visually appealing and realistic XR experiences. High-resolution displays and advanced graphics engines contribute to immersive visual fidelity.
Software Development Platforms
Software development platforms provide tools and frameworks for creating XR applications and experiences. These platforms simplify the development process, enabling developers to build immersive content.
XR’s versatility has led to its adoption across a wide range of industries:
Gaming and Entertainment
XR’s most prominent application is in gaming and entertainment. VR gaming offers immersive experiences that blur the lines between reality and virtual worlds. AR applications enhance real-world experiences with interactive overlays and engaging content.
Education and Training
XR provides immersive and interactive learning experiences, making education more engaging and effective. VR simulations can recreate real-world scenarios, allowing students to practice complex tasks in a safe and controlled environment. AR enhances classroom learning with interactive visualizations and augmented textbooks.
Healthcare
XR is transforming healthcare in numerous ways. VR therapy can treat phobias, anxiety, and PTSD. AR is used for surgical training, remote assistance, and patient education. MR facilitates complex surgical planning and real-time guidance during procedures.
Architecture and Design
XR enables architects and designers to visualize and experience their creations in immersive environments. VR walk-throughs allow clients to explore virtual buildings and spaces. AR allows designers to overlay virtual elements onto physical models.
Manufacturing and Engineering
XR is used for product design, prototyping, and assembly. VR simulations allow engineers to test and optimize designs before physical production. AR provides real-time guidance and information to workers on the factory floor.
Retail and Marketing
XR enhances the retail experience with virtual try-ons, product demonstrations, and interactive advertising. AR allows customers to visualize products in their homes before purchasing. VR creates immersive brand experiences and virtual showrooms.
Tourism and Heritage
XR is used to create virtual tours of historical sites and museums. AR enhances real-world tourism experiences with interactive overlays and information. VR allows users to explore remote or inaccessible locations.
Real estate
Virtual tours of properties, remote viewing of construction sites, and Augmented reality furniture placement for interior design.
Despite its immense potential, XR faces several challenges:
Hardware Limitations
Current XR hardware can be bulky, uncomfortable, and expensive. Technological advancements are needed to create more lightweight, comfortable, and affordable devices.
Content Development
Creating high-quality XR content is time-consuming and expensive. The development of user-friendly tools and platforms can streamline the content creation process.
Accessibility and Usability
XR experiences need to be accessible to a wider range of users, including individuals with disabilities. Intuitive interfaces and inclusive design principles are essential.
Social and Ethical Implications
The increasing prevalence of XR raises concerns about social isolation, privacy, and the potential for misuse. Ethical guidelines and regulations are needed to address these concerns.
Network Latency
For XR applications relying on cloud based processing, high network speeds and low latency is required. To properly allow for seemless experience.
The future of XR is bright, with ongoing research and development pushing the boundaries of immersive technology. As hardware becomes more advanced, software becomes more sophisticated, and content becomes more diverse, XR will continue to transform industries and reshape our lives. Key trends to watch include:
Increased adoption of 5G and cloud computing: These technologies will enable more powerful and seamless XR experiences.
XR technology is poised to revolutionize the way we interact with the world around us. By blending the physical and digital realms, XR opens up a world of possibilities, transforming industries, enhancing experiences, and shaping the future of human-computer interaction.



